
Spotify Technology S.A. employs its core competencies to maintain competitiveness in the global music streaming industry. This VRIO and VRIN analysis discusses such core competencies with regard to the resources and capabilities in the company’s digital content distribution value chain. Jay B. Barney posits that core competencies are valuable, rare, inimitable, and a resource or capability around which companies like Spotify are organized. Value, Rarity, Inimitability, and Organization are the basis of the VRIO analysis model, while the Non-substitutability variable is used instead of the Organization variable in the VRIN framework. In this VRIO analysis, VRIN analysis, and value chain analysis of Spotify, music streaming resources and capabilities are evaluated. In the resource-based view, core competencies and competitive advantages support the multinational expansion of the music streaming service. The VRIO framework also points to Spotify’s core competencies’ possible imitability, and the VRIN analysis points to possible substitutability of these competencies. The company’s strategic objectives must address the threat of imitation by further differentiating the business and its online services.
Spotify’s competitive position in the music streaming market is supported by resources and capabilities similar to the core competencies of major competitors, such as Apple Music, Google Play Music, Pandora, and Amazon Music. Along with Spotify, these competitors’ technological resources and capabilities maintain their respective major shares in the market. In this VRIO/VRIN analysis and value chain analysis, the core competencies pertain to competition with such major firms and smaller online service companies with limited operations. Using the resource-based view, Spotify’s organizational resources and capabilities and core competencies for business competitive advantages are listed in the following VRIN/VRIO analysis table.
Spotify VRIO & VRIN Analysis, Table (Resource-Based View)
| SPOTIFY’S ORGANIZATIONAL RESOURCES & CAPABILITIES | V | R | I | O | N |
| Competitive Parity or Equality: | |||||
| Wide market reach (all mobile users on iOS, android, etc.) | ✔ | ||||
| Wide accessibility (easily accessible online via apps & website) | ✔ | ||||
| Wide reach to all potential online advertisers | ✔ | ||||
| Tried-and-tested IT assets to support growing music streaming operations | ✔ | ||||
| Capable personnel for IT and creative work | ✔ | ||||
| Temporary Competitive Advantages: | |||||
| Established partnerships with a multitude of rights holders | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Strong operational presence in major markets | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Spotify’s Sustained Competitive Advantages (Core Competencies): | |||||
| High brand popularity | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Major streaming music market share leading to network effects | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Partnerships with major device manufacturers (Samsung smartphones and others) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
- This VRIN/VRIO analysis table is best viewed using HTML5-compatible browsers.
Spotify’s Non-core Competencies. Spotify’s competencies identified in this VRIO/VRIN analysis reflect the technological nature of the business and its value chain. In the resource-based view, the company’s non-core competencies are related to the information technologies supporting music platform operations. For example, wide market reach, wide accessibility, and wide reach to advertisers are all based on the automated and online nature of many of Spotify’s resources and capabilities. Based on the VRIN/VRIO analysis framework, these non-core competencies provide competitive parity or temporary competitive advantage because competitors possess the ability to develop similar technological competencies for the value chain operations of their respective online platforms. On the other hand, strong operational presence in major markets is a non-core organizational capability linked to Spotify’s corporate structure. Structural components correspond to the company’s offices in domestic or regional on-demand digital content markets. Moreover, personnel for IT and creative work are organizational resources linked to Spotify’s corporate culture. In the resource-based view, these non-core competencies are among the company’s resources and capabilities utilized in its value chain. However, as illustrated in the VRIO/VRIN analysis table, Spotify’s non-core competencies do not maintain sustained competitive advantages, especially when compared to digital content distribution competitors like Amazon and Apple.
VRIO Analysis of Spotify’s Core Competencies (Sustainable Competitive Advantages). This VRIO analysis of Spotify identifies three core competencies. In the resource-based view, these organizational resources and capabilities are the foundation of the company’s sustainable competitive advantages in the global music streaming industry. For example, Spotify’s brand is an organizational resource that provides sustainable or long-term competitive advantage for attracting more online platform users. This VRIO analysis also shows that the corporation’s major market share supports network effects, which is a characteristic of platform businesses and their value proposition. As Spotify’s user base population increases, so does the attractiveness of its online service and the value chain benefits to users. Having achieved a large international user network on the platform, the company enjoys strong sustainable competitive advantage, especially against smaller music streaming businesses. Also in this VRIO analysis of Spotify is the core competency of partnerships with device manufacturers. This organizational resource and capability strengthens the company’s market positioning and optimizes its value chain by making the online service the default in devices like Samsung smartphones. The SWOT analysis of Spotify Technology S.A. points out that these organizational resources and capabilities facilitate strategic management and planning to capitalize on available market opportunities. High brand popularity, major market share and network effects, and partnerships with manufacturers are enterprise resources and capabilities that satisfy the VRIO analysis criteria for core competencies. Considering the resource-based view of Spotify’s business operations, these music streaming core competencies determined through the VRIO framework also satisfy the VRIN framework’s criteria.
VRIN Analysis of Spotify’s Organizational Resources & Capabilities. A VRIN analysis of Spotify shows that the VRIO core competencies also satisfy the “N” (Non-substitutability) criterion for sustainable competitive advantage. In the VRIN/VRIO analysis table, all of the company’s VRIO resources and capabilities are also VRIN core competencies. For example, Spotify’s brand is an organizational resource that is non-substitutable because other resources or capabilities cannot replace the value of a strong digital content distribution brand. In the resource-based view, this core competency supports sustainable competitive advantage in marketing strategies based on the concept of brand recall, which helps in introducing new products and service functionality, or in attracting new subscribers. On the other hand, the major market share is a core competency included in this VRIN analysis of Spotify Technology S.A., referring to network effects and value chain optimization through user base growth. Long-term competitive advantage is created because the network effects of the company’s major market share cannot be easily substituted with non-platform operations and value chains of the same scale. Furthermore, the resource-based view of Spotify indicates strategic partnerships with major device manufacturers. In the VRIN framework, this core competency is a non-substitutable business capability for establishing market presence and intensifying market penetration by attracting more subscribers to the on-demand music streaming service. These core competencies, based on the VRIN analysis model, sustain value chain operational effectiveness for Spotify’s competitive advantages.
Spotify Value Chain Analysis: How the VRIN/VRIO Resources & Capabilities Relate to Spotify’s Value Chain
The core competencies that satisfy the requirements of the VRIO analysis framework and the VRIN analysis framework are the ones that have the most significant impact on Spotify’s value chain and competitive power. For example, the company’s major market share ensures network effects to maximize the value delivered to digital content creators (artists) and consumers (listeners/subscribers). Considering the resource-based view, as well as Michael E. Porter’s framework on competitive advantages and value chains, the following diagram represents the value chain analysis of Spotify Technology S.A.:
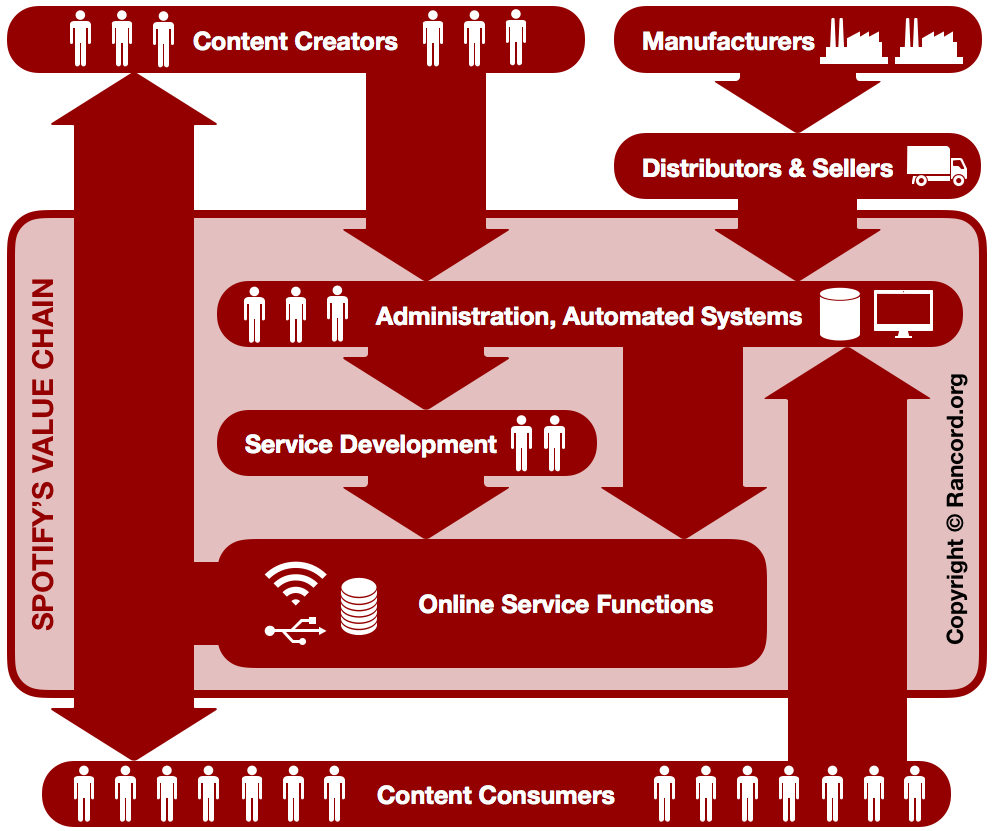
Spotify Technology S.A.’s business model, generic strategy, and intensive growth strategies determine the activities in its value chain. Manufacturers, distributors, and sellers are parties in the supply chain that delivers equipment for the company’s IT systems and databases. These parties are not inside Spotify’s value chain, but are in the digital content distribution industry’s value system (or “industry value chain”). This operational aspect requires supply chain analysis and management that strengthens the company’s value chain and competitive advantages by enhancing the value delivered to content creators and consumers. Furthermore, in the value chain diagram, value-adding activities (administration and automated systems, service development, and online service functions) sustain Spotify’s competitive advantage by optimizing user experience. These same value chain activities utilize user-generated data to develop the service and enhance customer satisfaction. Considering the resource-based view, the company’s VRIO & VRIN core competencies are used in the value chain activities to fulfill the value proposition, which is to support artists’ livelihood and enable fans to access creative work, according to Spotify’s corporate mission and vision statements. This value chain analysis shows that the utilization of VRIN & VRIO resources and capabilities in Spotify’s value chain is a form of servitization, where the product is digital content, and the service includes playlist curation and online IT maintenance and administration.
Key Points: VRIO Analysis, VRIN Analysis & Value Chain Analysis of Spotify Technology S.A.
VRIN Analysis & VRIO Analysis. According to the VRIN and VRIO frameworks, Spotify’s organizational resources and capabilities support competitive advantages that depend on network effects in platform business operations. Aside from core competencies like the company’s brand, network effects increase value chain effectiveness and, consequently, the online service’s value, as the user base grows. Strategies for improving Spotify’s business operations must integrate strategic initiatives to sustain the platform’s network effects. Long-term business success depends on these network effects in on-demand streaming platform operations. Applying the resource-based view, Spotify’s VRIO and VRIN core competencies are essential for maintaining a leading strategic position in the international on-demand digital content market.
Value Chain Analysis. The top-level view of value-adding activities shown in the value chain analysis diagram of Spotify’s business indicates a cycle that makes the online streaming service more valuable. This cycle represents the network effects of the online platform: users benefit from Spotify’s service value, and the company benefits from user-generated data. This cycle reinforces the company’s value proposition, leading to sustained competitive advantages. In the resource-based view, the VRIN and VRIO core competencies are used within this cycle in Spotify’s value chain. Strategically developing these core organizational resources and capabilities strengthens the company’s competitive position as a leading streaming music service provider. Similarly, developing new core competencies can help keep Spotify’s leading industry position.
References
- Ayub, A., Razzaq, A., Aslam, M. S., & Iftekhar, H. (2013). A conceptual framework on evaluating SWOT analysis as the mediator in strategic marketing planning through marketing intelligence. European Journal of Business and Social Sciences, 2(1), 91-98.
- Bhargava, A., Bafna, A., & Shabarisha, N. (2018). A Review on Value Chain Analysis as a Strategic Cost Management Tool. Account and Financial Management Journal, 3(03), 1386-1393.
- Fahy, J., & Hooley, G. (2002). Sustainable competitive advantage in electronic business: Towards a contingency perspective on the resource-based view. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 10(4), 241-253.
- Having rescued recorded music, Spotify may upend the industry again. The Economist.
- International Trade Administration of the U.S. Department of Commerce – The Media and Entertainment Industry in the United States.
- Jackson, S. E., Joshi, A., & Erhardt, N. L. (2003). Recent research on team and organizational diversity: SWOT analysis and implications. Journal of Management, 29(6), 801-830.
- Morris, J. W., & Powers, D. (2015). Control, curation and musical experience in streaming music services. Creative Industries Journal, 8(2), 106-122.
- Mudambi, R., & Puck, J. (2016). A global value chain analysis of the ‘regional strategy’ perspective. Journal of Management Studies, 53(6), 1076-1093.
- Park, N. K., Mezias, J. M., & Song, J. (2004). A resource-based view of strategic alliances and firm value in the electronic marketplace. Journal of Management, 30(1), 7-27.
- Pesic, M. A., Milic, V. J., & Stankovic, J. (2013). Application of VRIO framework for analyzing human resources’ role in providing competitive advantage. Tourism & Management Studies, 575-586.
- Schroeder, A., & Kotlarsky, J. (2015). Digital resources and their role in advanced service provision: A VRIN analysis. In Proceedings of the Spring Servitization Conference (pp. 67-74). Aston University.
- Spotify Technology S.A. – Privacy Center – Spotify uses personal data to create the best listening experience.
- Spotify Technology S.A.’s Annual Report to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (Form 20-F).
- Spotify Technology S.A.’s Report of Foreign Private Issuer to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (Form 6-K).
- Spotify Technology S.A.’s Website.
- Talaja, A. (2012). Testing VRIN framework: Resource value and rareness as sources of competitive advantage and above average performance. Management: Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 17(2), 51-64.
- Yu, Y., Wang, X., Zhong, R. Y., & Huang, G. Q. (2016). E-commerce logistics in supply chain management: Practice perspective. Procedia CIRP, 52, 179-185.
